Hip Replacement
ANATOMY OF THE HIP JOINT
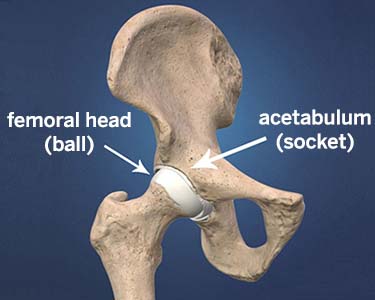
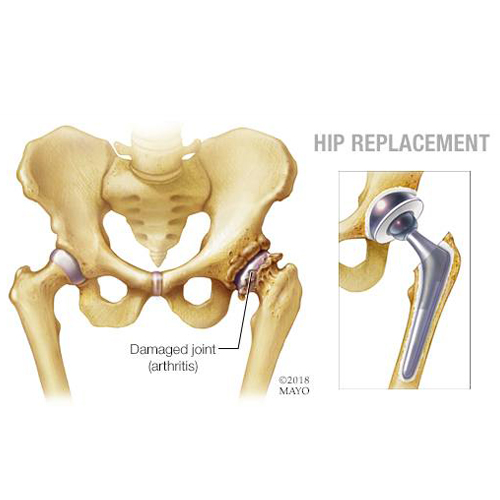
The hip joint is a ‘ ball and socket’ joint. The hip joint allows movement to occur between the thigh bone (Femur), and the hip bone (Pelvis). The pelvis contains the ‘socket’ called the acetabulum. The ball shaped head of the femur fits into the acetabulum, forming a ball and socket joint which enables the leg to have a wide range of movements.
The outer surface of the femoral head and the inside surface of the acetabulum are covered with cartilage. The cartilage surface is a tough and very smooth material that allows the two surfaces to slide against one another during movement with ease.
Hip joint replacement surgery involves replacing the Head of the femur (ball) and the acetabulum (socket) with man-made components, called prostheses. The hip prostheses are designed to simulate the human anatomy as closely as possible.
COMPONENTS OF HIP REPLACEMENT
Besides the Conventional Hip Replacement alluded to above, there are certain variations base on the primary presenting pathology, patient profile, Bone and soft tissue quality and cost implications.
BIPOLAR Hip Replacement
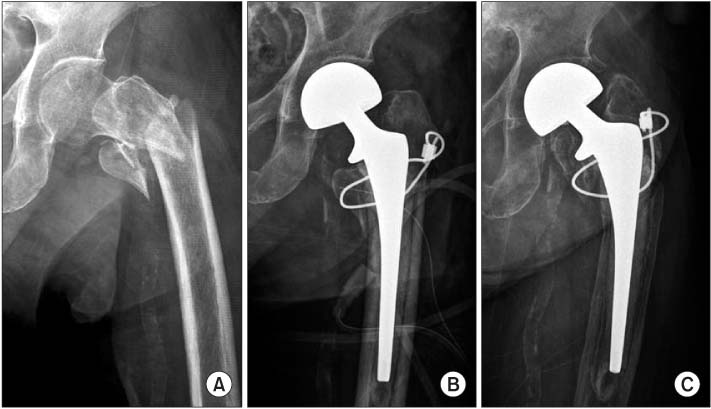
In this case, usually post Hip Fractures-Only the Femoral Component is replaced with a Special Bipolar Head to compensate for the fractured femoral Neck. The Acetabulum is not replaced and this type of hip replacement is reserved for the elderly with limited life expectancy.
Dual Mobility Hip Replacement
In this Type of Hip Replacement, Both the acetabulum(socket)and the femur are replaced, but the acetabulum is of a semi constrained variety to increase stability of the replaced hip. This is the treatment of choice in patients with Parkinsonism, Dementia and other Neuro muscular Issues. It is also an option in Complex Primary or Revision Hip Scenarios where the surrounding soft tissue envelope is compromised-to increase stability and reduce dislocation risks.
TYPES OF HIP REPLACEMENT
Each hip prosthesis is made up of several parts:
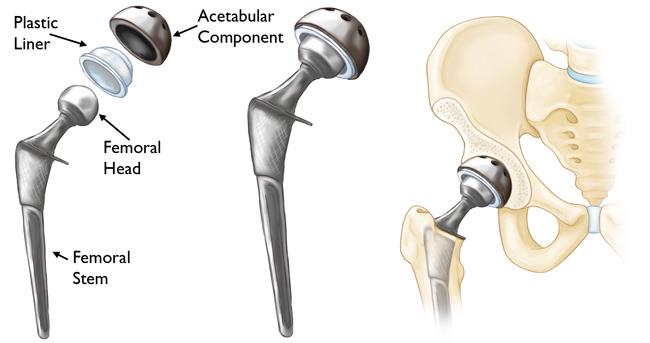
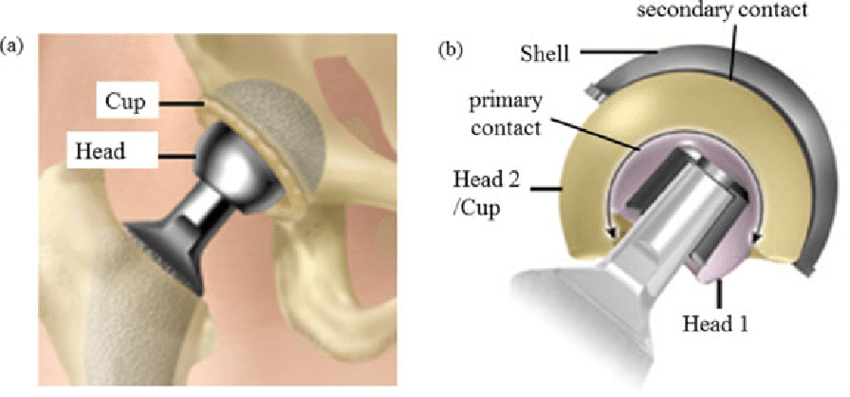
The acetabular component or cup replaces the acetabulum. The acetabular component can either be made of a metal alloy outer shell with a fitted plastics, metal or ceramic liner or it can be made of a single plastic component. The acetabular component is either a press fit component with or without supplementary screw fixation –UNCEMENTED ACETABULUM, or A single Polyethylene (Plastic) component fixed to the bone with cement-CEMENTED ACETABULUM The femoral component replaces the femoral Head. It can again be either cemented or uncemented similar to the acetabular options as above—A combination of cemented and Uncemented components can be used as per the patient’s bone quality and the pathology for which the Replacement is being performed. The Femoral component whether with Cement or without, consists of a femoral stem with a modular head which could be Ceramic or Metal. The currently available options include ceramic-ceramic, polyethylene-ceramic and polyethylene -metal articulations, chosen as per patient profile, longevity and cost implications.
INDICATIONS FOR HIP REPLACEMENT
Primary Hip Replacement
There are a number of conditions that can result in a patient having to undergo hip replacement surgery. Perhaps the most common condition is osteoarthritis that is commonly referred to as ‘wear and tear arthritis’. Osteoarthritis can occur with no previous history of injury to the hip joint. The hip simply ‘wears out’. There may be a genetic tendency in some people that increases their chances of developing osteoarthritis.
Avascular necrosis is another condition that could lead to hip replacement surgery. In this condition, the femoral head (ball) loses a portion of its blood supply and actually dies. This leads to collapse of the femoral head and degeneration of the hip joint. Avascular necrosis has been linked to alcoholism, fractures and dislocations of the hip, and long-term steroid treatment for other diseases. But in more than 80% cases the cause may not be known. It usually affects both Hips, though not symmetrically. This condition is a more common reason for Hip Replacement than Degenerative Hip Arthritis in the Indian Scenario.
Complex Primary Hip Replacement
This category alludes to problems of hip joint function secondary to Failed hip fracture fixation which needs to be converted to Hip Replacement, Childhood hip Pathologies, previously operated leading to early hip degeneration needing hip replacement. Other examples of complex primary hip replacement include Ankylosed or Fused hips due to Inflammatory joint disease needing conversion to Hip Replacement to impart mobility and improve ambulation and Infective Hip disease where a single or two stage Hip Replacement may be necessary.
Revision Hip Replacement
A Hip replacement done for any indication as above can go WRONG!!, the commonest causes being infection, instability, Early component wear and periprosthetic fractures around the previous Hip replacement. All these conditions cause increased morbidity and necessitate repeat or revision hip replacement. This requires a high level of experience and expertise and is certainly not for the faint hearted. The results of Revision Hip Replacement surgery are progressively improving with better Implant inventory and techniques, now coming close to primary replacement results, albeit at higher costs and associated morbidity.
Aims of a HIP Replacement
- The aim of hip replacement surgery is to:
- Relieve your pain.
- Correct any deformity.
- Provide stability to your joint.
- Restore loss of function in your hip.
- Equalise leg length, if possible.
- Improve your quality of life.
FAQ's On Hip Replacement
What exercises I need to do after surgery?
What are the disadvantages of this operation?
There is less than 1% chance of infection in the world’s best centers. We match the international standards by having strict operation theatre protocol, antibiotics, infection control team and discipline in the ward itself. Other complications are minor and it is possible to avoid if you strictly follow the advice of your doctor and therapists.
There is a risk of Hip instability or dislocation, more so in revision hip surgery-1 to 2%, hence absolutely mandatory that certain Hip Protocols need to be followed in the early post-operative period for better outcomes.
How long an artificial joint last?
We give an average life span of about 10-15 years. But the longest surviving artificial joint is 40 years in the world. It also depends on how you take care of your new joint.
Will it affect my day-to-day life?
The surgery will lead to better quality of life and you can do your day-to-day activities normally. Post Hip Replacement surgery, certain permanent restrictions need to be adhered to—No ground level sitting, No sitting cross legged and to avoid squatting(i.e. not to use Indian style Toilet)
