Components Of Hip Replacement
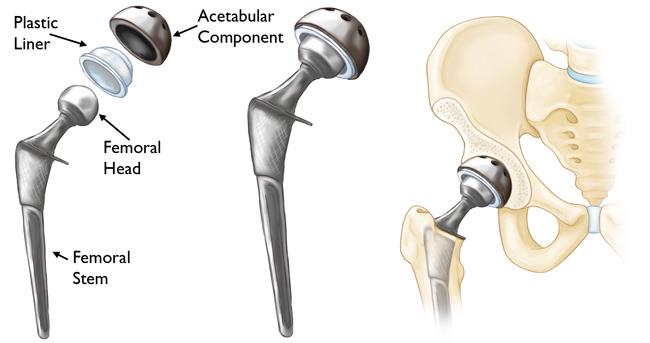 Each hip prosthesis is made up of several parts:
Each hip prosthesis is made up of several parts:The acetabular component or cup replaces the acetabulum. The acetabular component can either be made of a metal alloy outer shell with a fitted plastics, metal or ceramic liner or it can be made of a single plastic component. The acetabular component is either a press fit component with or without supplementary screw fixation –UNCEMENTED ACETABULUM, or A single Polyethylene (Plastic) component fixed to the bone with cement-CEMENTED ACETABULUM
The femoral component replaces the femoral Head. It can again be either cemented or uncemented similar to the acetabular options as above—A combination of cemented and Uncemented components can be used as per the patient’s bone quality and the pathology for which the Replacement is being performed. The Femoral component whether with Cement or without, consists of a femoral stem with a modular head which could be Ceramic or Metal. The currently available options include ceramic-ceramic, polyethylene-ceramic and polyethylene -metal articulations, chosen as per patient profile, longevity and cost implications.
Besides the Conventional Hip Replacement alluded to above, there are certain variations base on the primary presenting pathology, patient profile, Bone and soft tissue quality and cost implications.
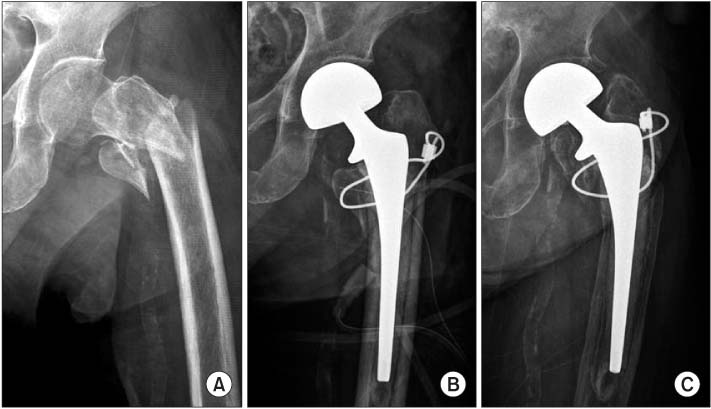
BIPOLAR Hip Replacement
In this case, usually post Hip Fractures-Only the Femoral Component is replaced with a Special Bipolar Head to compensate for the fractured femoral Neck. The Acetabulum is not replaced and this type of hip replacement is reserved for the elderly with limited life expectancy.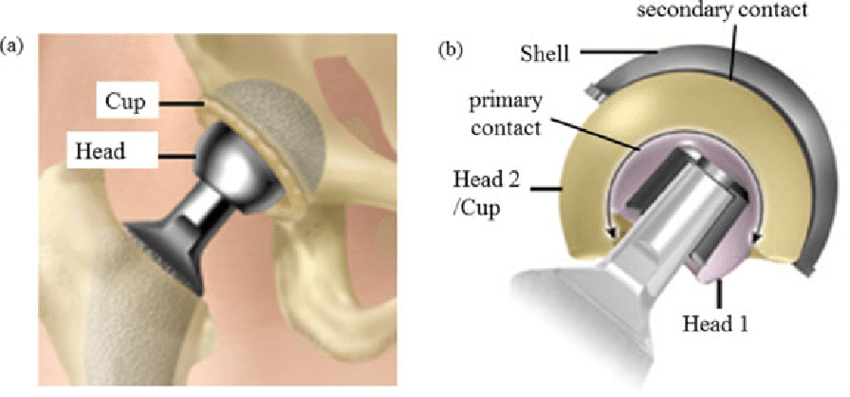
Dual Mobility Hip Replacement
In this Type of Hip Replacement, Both the acetabulum(socket)and the femur are replaced, but the acetabulum is of a semi constrained variety to increase stability of the replaced hip. This is the treatment of choice in patients with Parkinsonism, Dementia and other Neuro muscular Issues. It is also an option in Complex Primary or Revision Hip Scenarios where the surrounding soft tissue envelope is compromised-to increase stability and reduce dislocation risks.
Besides the Conventional Hip Replacement alluded to above, there are certain variations base on the primary presenting pathology, patient profile, Bone and soft tissue quality and cost implications.

BIPOLAR Hip Replacement
In this case, usually post Hip Fractures-Only the Femoral Component is replaced with a Special Bipolar Head to compensate for the fractured femoral Neck. The Acetabulum is not replaced and this type of hip replacement is reserved for the elderly with limited life expectancy.
Dual Mobility Hip Replacement
In this Type of Hip Replacement, Both the acetabulum(socket)and the femur are replaced, but the acetabulum is of a semi constrained variety to increase stability of the replaced hip. This is the treatment of choice in patients with Parkinsonism, Dementia and other Neuro muscular Issues. It is also an option in Complex Primary or Revision Hip Scenarios where the surrounding soft tissue envelope is compromised-to increase stability and reduce dislocation risks.
Besides the Conventional Hip Replacement alluded to above, there are certain variations base on the primary presenting pathology, patient profile, Bone and soft tissue quality and cost implications.

BIPOLAR Hip Replacement
In this case, usually post Hip Fractures-Only the Femoral Component is replaced with a Special Bipolar Head to compensate for the fractured femoral Neck. The Acetabulum is not replaced and this type of hip replacement is reserved for the elderly with limited life expectancy.
Dual Mobility Hip Replacement
In this Type of Hip Replacement, Both the acetabulum(socket)and the femur are replaced, but the acetabulum is of a semi constrained variety to increase stability of the replaced hip. This is the treatment of choice in patients with Parkinsonism, Dementia and other Neuro muscular Issues. It is also an option in Complex Primary or Revision Hip Scenarios where the surrounding soft tissue envelope is compromised-to increase stability and reduce dislocation risks.
